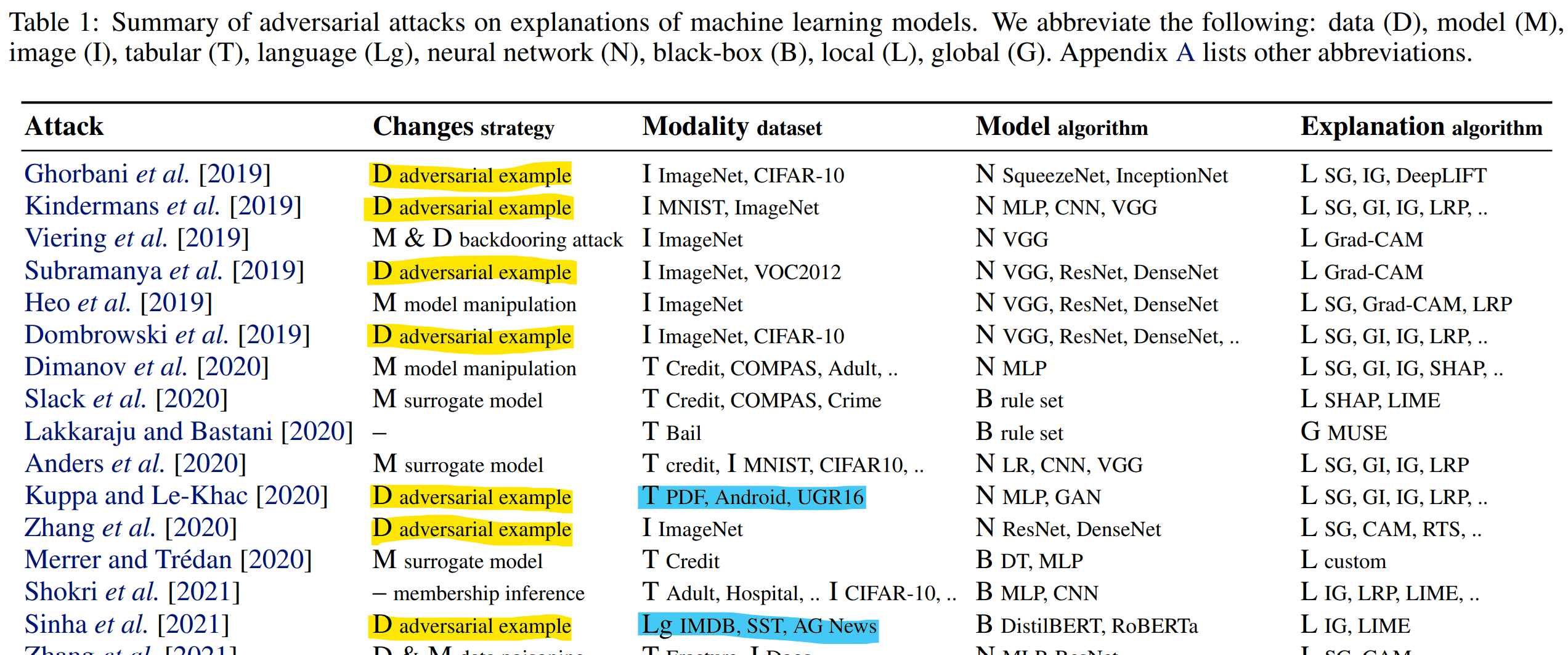
Adversarial Attacks and Defenses in XAI: A Survey
Hubert Baniecki, Przemyslaw Biecek
University of Warsaw, Poland
IJCAI 2023 Workshop on XAI, Macao, SAR
August 31, 2023
Acknowledgements

This work was financially supported by the Polish National Science Centre grant number 2021/43/O/ST6/00347.
Prologue
I am a PhD student in computer science/XAI interested in adversarial attacks and evaluation protocols.
Disclaimer: Parts of this presentation come from other published work.

Contributions & comments are welcomed!
Write me at h.baniecki@uw.edu.pl
Why a survey paper?

Dombrowski et al. Explanations can be manipulated and geometry is to blame. NeurIPS 2019
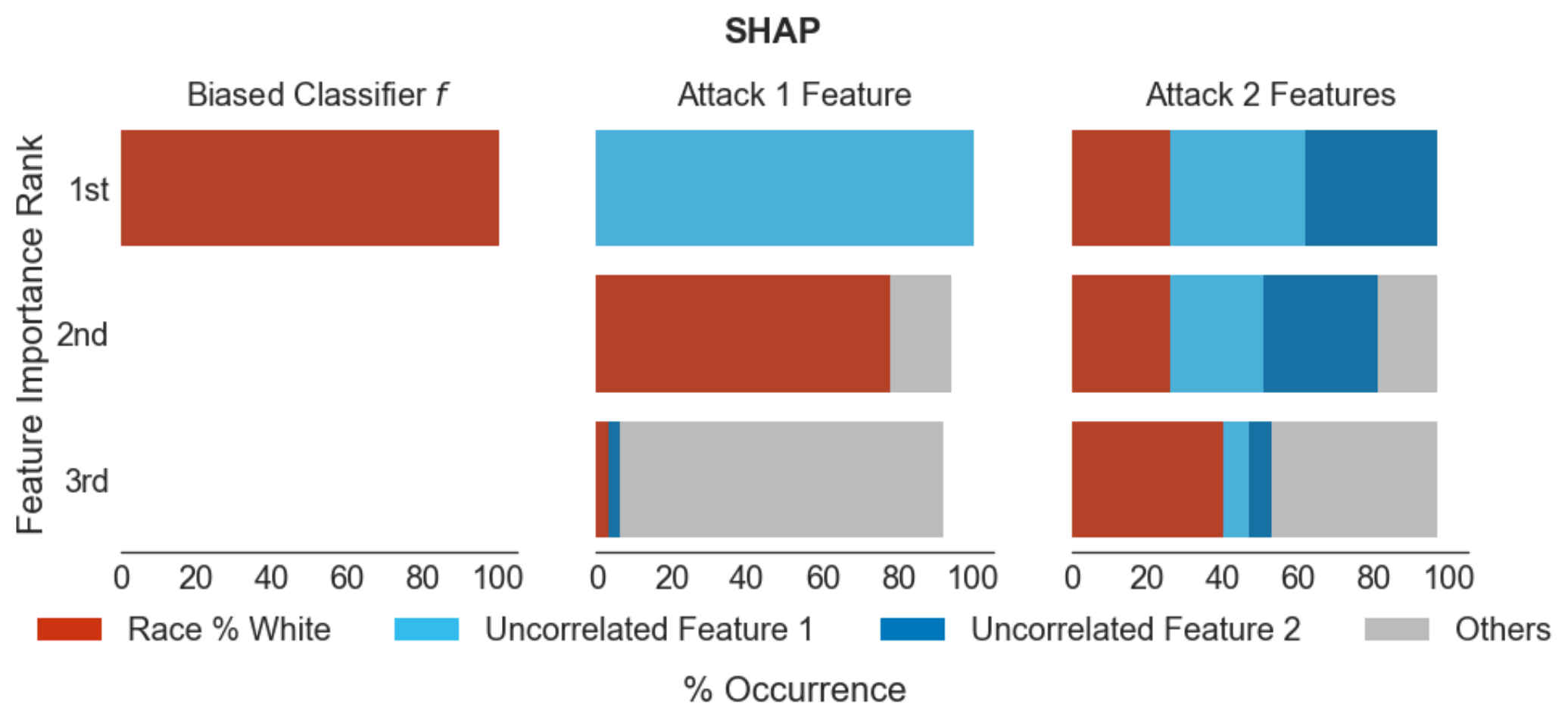
Slack et al. Fooling LIME and SHAP: Adversarial Attacks on Post hoc Explanation Methods. AIES 2020
Adversarial ML vs. Explainable AI
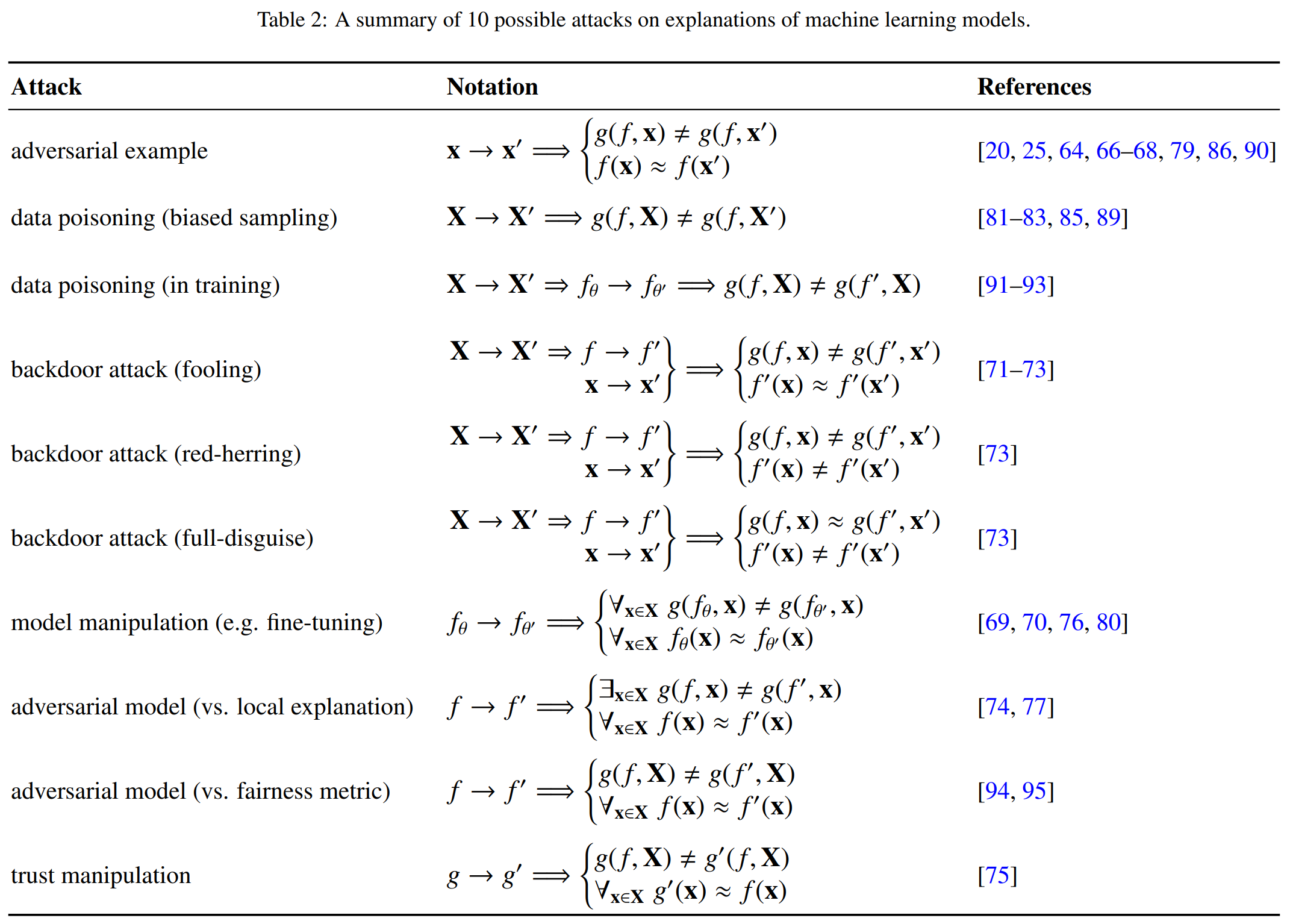
Attack: adversarial example
For a prediction:
\[ \mathbf{x} \rightarrow \mathbf{x}' \Longrightarrow f(\mathbf{x}) \neq f(\mathbf{x}') \] where \(\rightarrow\) may be an “invisible’’ data perturbation.
What about an explanation?
\[ g(f,\mathbf{x}) \]
\[ g(f,\mathbf{x}) := \mathbf{x} \odot \frac{\partial f(\mathbf{x})}{\partial \mathbf{x}} \]
\[ g(f,\mathbf{x}) := \mathbf{x} \odot \frac{\partial f(\mathbf{x})}{\partial \mathbf{x}} \\ \mathbf{\color{blue} x} \rightarrow \mathbf{\color{red} x}' \Longrightarrow g(f,\mathbf{\color{blue} x}) \neq g(f,\mathbf{\color{red}x'}) \]
\[ g(f,\mathbf{x}) := \mathbf{x} \odot \frac{\partial f(\mathbf{x})}{\partial \mathbf{x}} \\ \mathbf{\color{blue} x} \rightarrow \mathbf{\color{red} x'} \Longrightarrow \left\{\begin{array}{@{}l@{}} g(f,\mathbf{\color{blue} x}) \neq g(f,\mathbf{\color{red} x'}) \\ f(\mathbf{\color{blue} x}) \approx f(\mathbf{\color{red} x'}) \\ \end{array}\right. \]

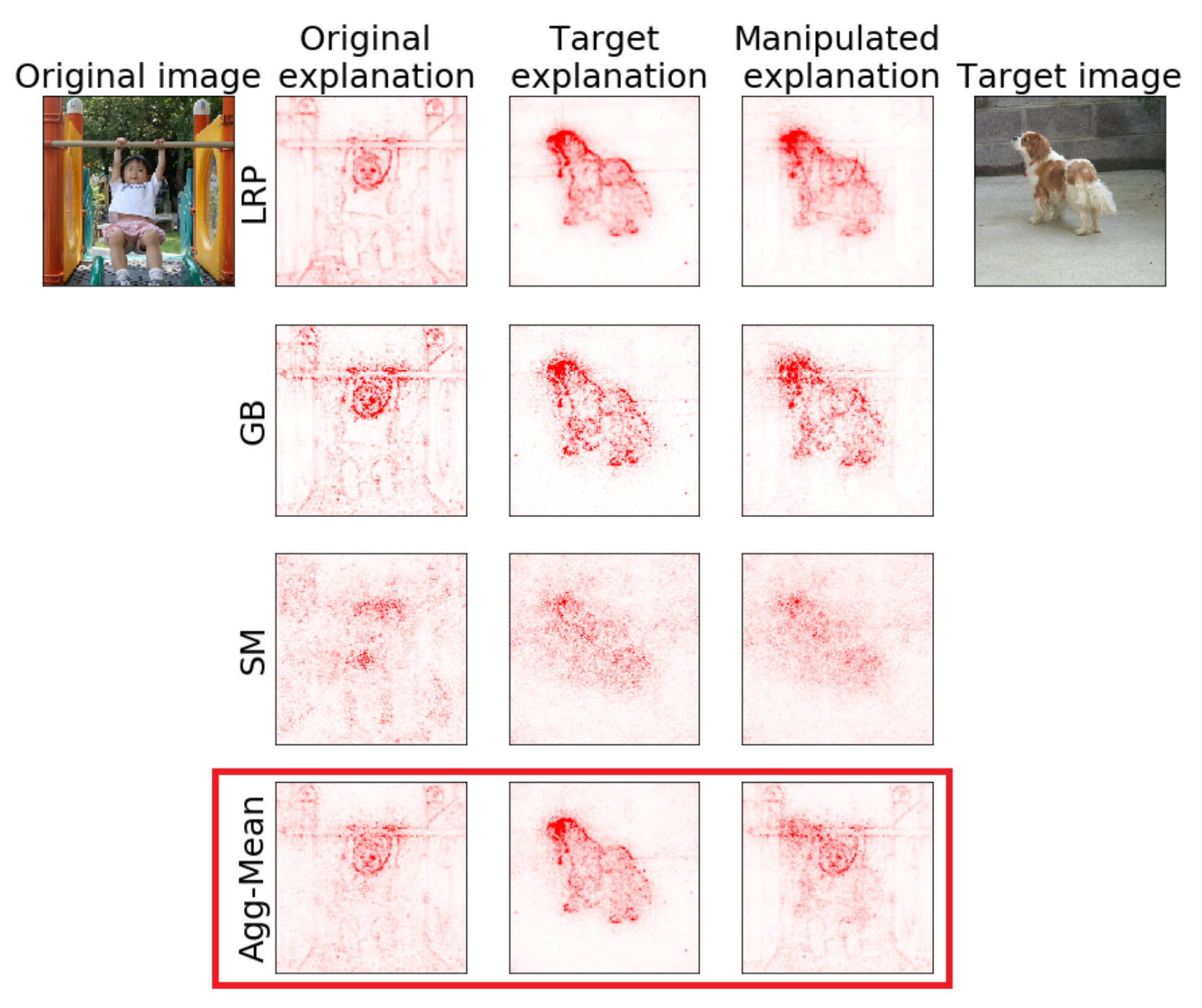
Dombrowski et al. Explanations can be manipulated and geometry is to blame. NeurIPS 2019
Attack: adversarial example (cont.)
How to find \(\mathbf{\color{blue} x} \rightarrow \mathbf{\color{red} x'}\)? An optimization problem.
- For neural networks*: use gradients
*differentiable models and explanation methods
- For black-box models with model-agnostic explanations:
use genetic algorithms
Defense? Prevention
\[ \mathbf{\color{blue} x} \rightarrow \mathbf{\color{red} x'} \Longrightarrow \left\{\begin{array}{@{}l@{}} g(f,\mathbf{\color{blue} x})\;{\color{green} \approx}\; g(f,\mathbf{\color{red} x'}) \\ f(\mathbf{\color{blue} x}) \approx f(\mathbf{\color{red} x'}) \\ \end{array}\right. \]
- explanation aggregation
\(g(f,\mathbf{\color{blue} x}) \neq g(f,\mathbf{\color{red} x'})\;\) but \(\;{\color{green}h}(f,\mathbf{\color{blue} x})\;{\color{green} \approx}\; {\color{green}h}(f,\mathbf{\color{red} x'})\) - model regularization
\(g(f,\mathbf{\color{blue} x}) \neq g(f,\mathbf{\color{red} x'})\;\) but \(\;g({\color{green}f'},\mathbf{\color{blue} x})\;{\color{green} \approx}\; g({\color{green}f'},\mathbf{\color{red} x'})\) - robustness, stability, uncertainty, …
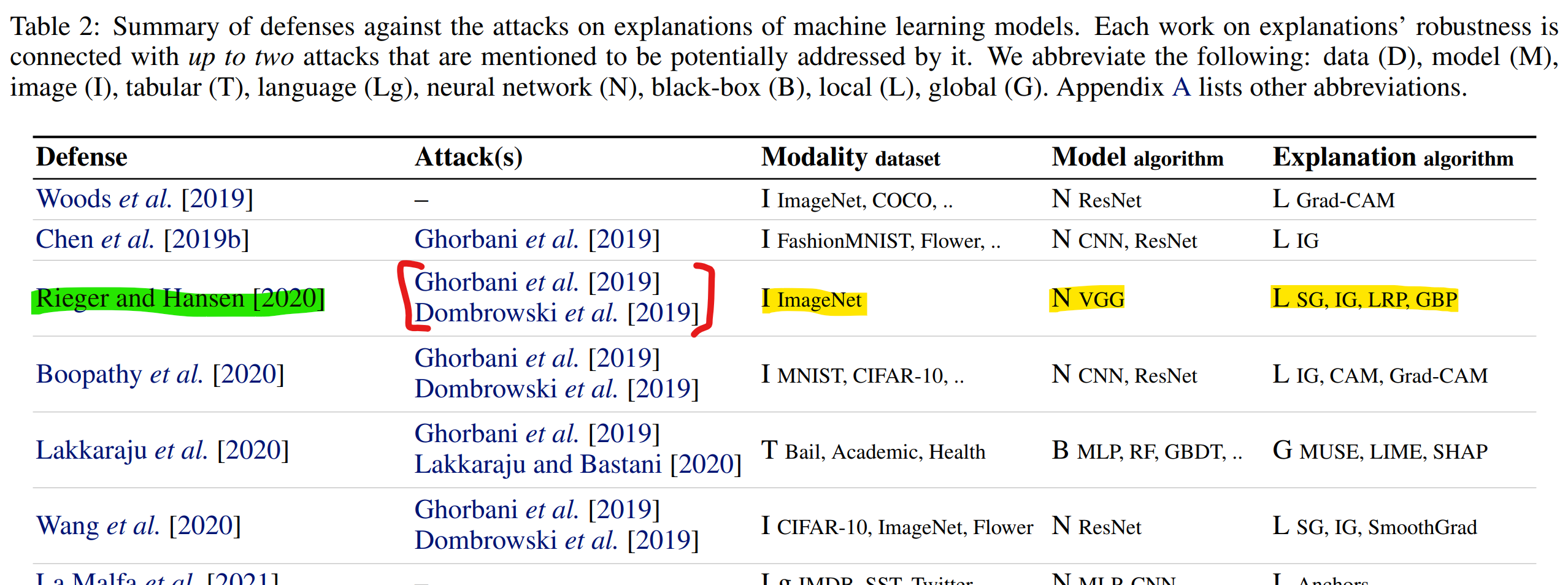
Defense: explanation aggregation
\(g(f,\mathbf{\color{blue} x}) \neq g(f,\mathbf{\color{red} x'})\;\) but \(\;{\color{green}h}(f,\mathbf{\color{blue} x})\;{\color{green} \approx}\; {\color{green}h}(f,\mathbf{\color{red} x'})\); \(\;{\color{green}k}(f,\mathbf{\color{blue} x})\;{\color{green} \approx}\; {\color{green}k}(f,\mathbf{\color{red} x'})\)
 Rieger & Hansen. A simple defense against adversarial attacks on heatmap explanations. ICML WHI 2020
Rieger & Hansen. A simple defense against adversarial attacks on heatmap explanations. ICML WHI 2020
Defense: model regularization
\(g(f,\mathbf{\color{blue} x}) \neq g(f,\mathbf{\color{red} x'})\;\) but \(\;g({\color{green}f'},\mathbf{\color{blue} x})\;{\color{green} \approx}\; g({\color{green}f'},\mathbf{\color{red} x'})\)
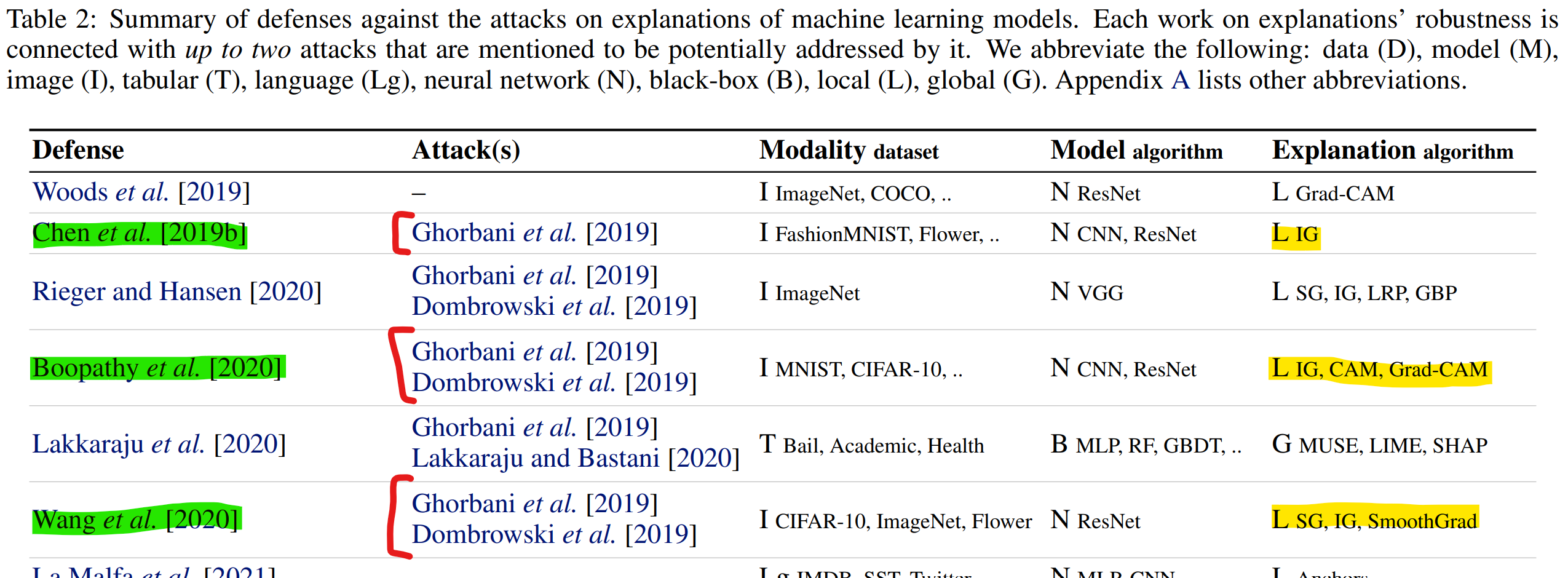
A chain of works improving the robustness of explanations.
Survey: systematization, research gaps, future work
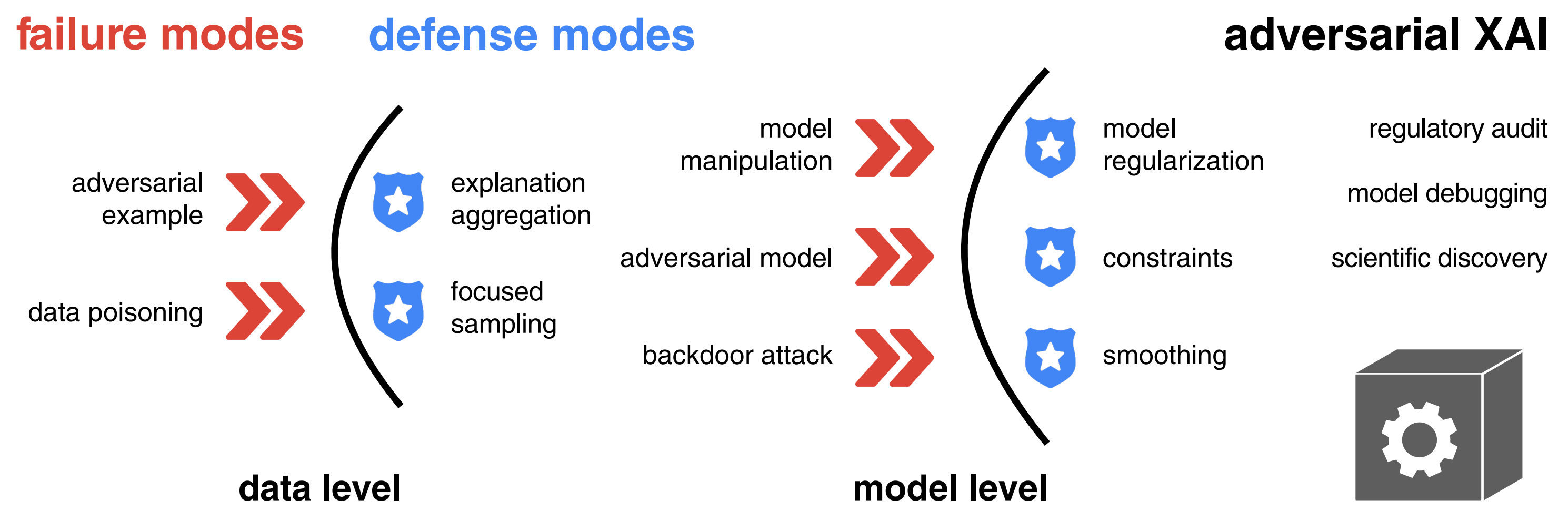
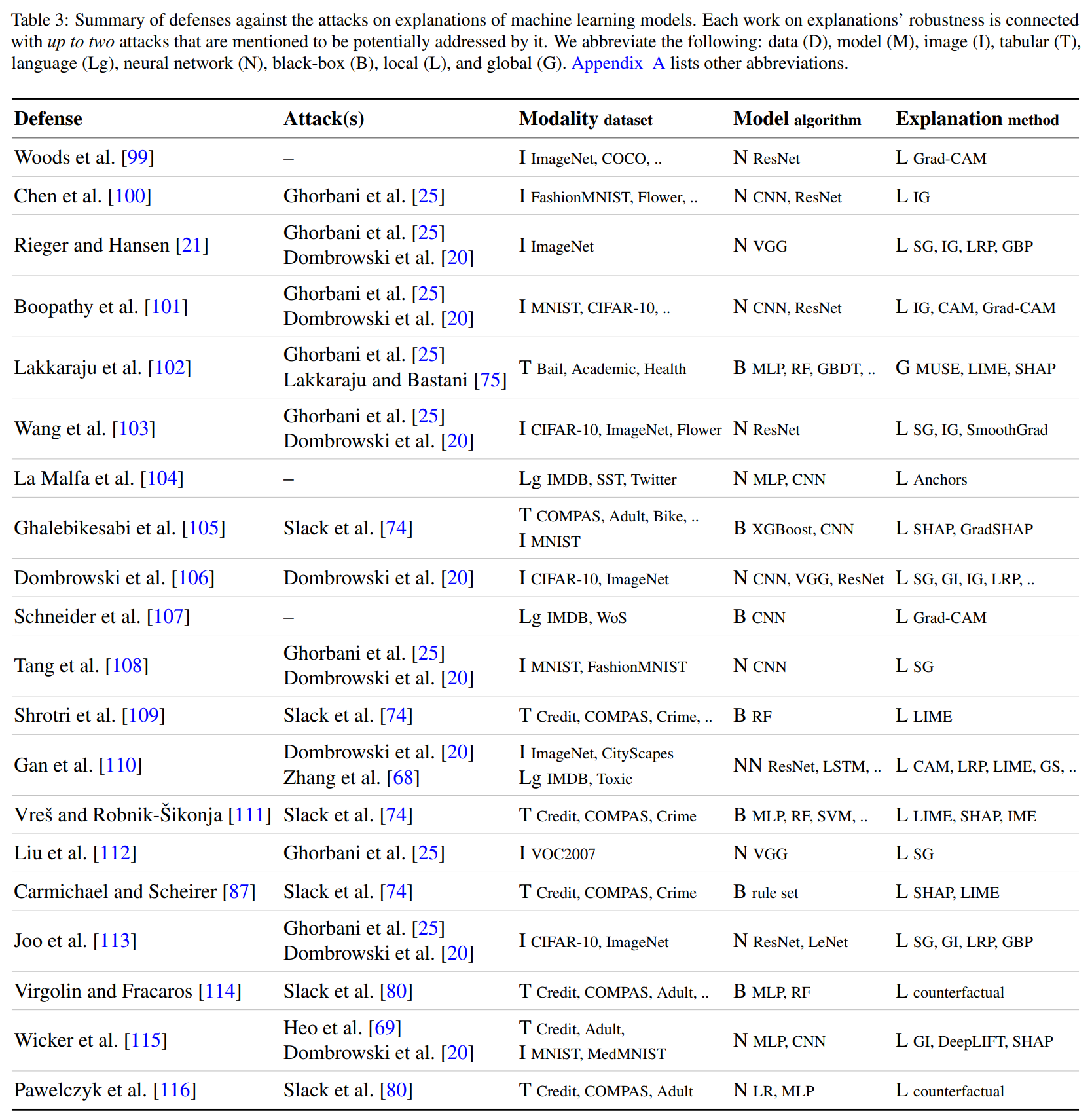
Systematization of the attacks

Extended version (to appear on arXiv):
Insecurities in Explainable AI
Future directions in Adversarial XAI
- Attacks on: more recent explanation algorithms, explainable
“by-design’’ machine learning models, bypass the defense (attack\(^2\)) - Defenses: prevent current insecurities in XAI, improve explanation algorithms (robustness), update safety & evaluation protocols
- AdvXAI beyond the image and tabular data modalities.
- AdvXAI beyond classical models towards transformers.
- Ethics, impact on society, and law concerning AdvXAI.
- (No) Software, datasets and benchmarks.
GitHub list since 2020
Next: submit the extended version to a journal.
References
- H. Baniecki, P. Biecek. Adversarial Attacks and Defenses in Explainable Artificial Intelligence: A Survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.06123.
- Dombrowski et al. Explanations can be manipulated and geometry is to blame. NeurIPS 2019
- Slack et al. Fooling LIME and SHAP: Adversarial Attacks on Post hoc Explanation Methods. AIES 2020
- Rieger & Hansen. A simple defense against adversarial attacks on heatmap explanations. ICML WHI 2020
Hubert Baniecki – AdvXAI – slides: hbaniecki.com/ijcai2023 – lab: mi2.ai